What are Coagulants?
- Coagulants are chemical substances that promote the destabilization of suspended particles in wastewater.
- They neutralize the electrical charges on particles, causing them to come together and form larger aggregates.
- Coagulants are chemicals that are added to wastewater to destabilize colloidal particles and other small suspended particles that are hard to remove by settling alone.
- They work by neutralizing the electrical charges on particles, allowing them to come together and form larger clumps or aggregates.
- Common coagulants include aluminum sulphate (alum), ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride (PAC). These chemicals are usually added early in the treatment process.
What are Flocculants?
- Flocculants, on the other hand, enhance the size and weight of these aggregates, leading to the formation of floccules.
- These floccules settle more easily and can be separated from the water, resulting in improved water clarity.
- Flocculants are chemicals that are added after coagulation. They, facilitate the aggregation of already coagulated particles into larger, heavier flocs.
- Flocculants help to further enhance the settling or flotation of these flocs, making it easier to separate them from the treated water.
- Common flocculants include polyacrylamides and polymers.
How does Flocculants work?
- Flocculants work by creating bridges between already coagulated particles. These bridges are formed due to the molecular structure of the flocculants chemicals.
- When added to the water, flocculants attach to the surfaces of coagulated particles, causing them to stick together.
- This process forms larger and denser flocs that are more easily separated from the water through sedimentation or flotation processes.
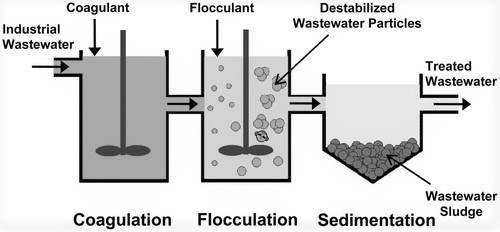
Coagulant vs. Flocculants
Coagulants and flocculants are both chemicals used in water and wastewater treatment, but they serve different purposes in the clarification and purification of water. Here’s a more detailed comparison between coagulants and flocculants:
- Coagulants Purpose: Coagulants are primarily used to destabilize colloidal and suspended particles in water. They promote the aggregation of fine particles by neutralizing their electrical charges, allowing them to come together and form larger, heavier particles called flocs.
- Application Stage: Coagulants are typically added early in the water treatment process, often right after the initial screening and primary settling stages. Their role is to initiate the process of particle aggregation, making it easier to remove impurities from the water.
- Common Coagulants: Common coagulants include aluminum sulphate (alum), ferric chloride, polyaluminum chloride (PAC), and other metal salts.
- Function: Coagulants act as “coagulators,” bringing together small particles and colloids into larger clumps or aggregates.
Flocculants are used to further enhance the aggregation of already coagulated particles.
- Flocculants Purpose: They aid in forming larger, denser flocs from the coagulated particles, making the removal of impurities more efficient.
- Application Stage: Flocculants are added later in the treatment process, following the addition of coagulants. They play a role in the secondary treatment of the water, ensuring that the coagulated particles settle or float effectively.
- Common Flocculants: Common flocculants include polyacrylamides, polymers, and organic compounds with high molecular weights.
- Function: Flocculants act as “bridges” between already coagulated particles, promoting further aggregation. They create bonds between particles, forming larger, heavier flocs that are easier to separate from the treated water through sedimentation or flotation.
What are Flocculants Coagulants in Wastewater Treatment?
Coagulants and flocculants are chemicals used in wastewater treatment to help remove suspended particles and impurities from water, making it suitable for discharge or reuse. They play distinct but complementary roles in the treatment process.
How does a water treatment facility work?
A water treatment facility works by:
- Screening: Removing large debris from raw water.
- Coagulation: Adding chemicals to clump small particles into flocs.
- Flocculation: Enhancing floc formation.
- Sedimentation: Allowing flocs to settle.
- Filtration: Passing water through filters to remove remaining impurities.
- Disinfection: Treating with chemicals to kill pathogens.
- Storage & Distribution: Storing and delivering clean water.
- Sludge Treatment: Managing waste generated.
- Quality Monitoring: Continuously ensuring water meets standards.
How do Coagulants Destabilize Suspended particles in Wastewater?
- Coagulants work by introducing charges opposite to those of the suspended particles in the wastewater.
- This neutralizes the repulsive forces between particles, allowing them to come closer together.
- As the particles approach each other, van der Waals forces and chemical bridging occur, promoting aggregation and the formation of larger, settle able particles.
What role do Coagulants play in Promoting the Formation of Settle able Particles?
- Coagulants neutralize the electrical charges on suspended particles, reducing the repulsive forces between them.
- This neutralization destabilizes the particles, allowing them to collide and form larger aggregates that are more likely to settle under the influence of gravity or other separation mechanisms.
How do Flocculants Enhance the Size and Weight of Particle Aggregates?
- Flocculants are high-molecular-weight polymers that act as binding agents, causing smaller particle aggregates to come together and form larger clusters known as floccules.
- The flocculants bridge the gaps between particle aggregates, promoting further growth and consolidation of the floccules.
- This increases their size and weight, making them easier to separate from the water.
What are the Advantages of using Flocculants in Wastewater Treatment?
- Flocculants significantly improve the efficiency of sedimentation or filtration processes in wastewater treatment.
- By promoting the formation of larger and denser floccules, flocculants enhance the settling characteristics of suspended particles, resulting in improved clarification and solids removal.
- Flocculants also improve the effectiveness of filtration processes by aiding in the formation of larger particles that are easier to capture and remove from the water.
How do Coagulants and Flocculants work Synergistically to Improve Treatment Efficiency?
- Coagulants and flocculants have complementary functions in the wastewater treatment process.
- Coagulants initiate the aggregation process by neutralizing charges and promoting particle collision, while flocculants enhance the growth and consolidation of particle aggregates into larger flocks.
- This synergistic action improves the overall treatment efficiency by facilitating the formation of settle able particles, leading to better separation and removal of contaminants from the water.
What factors should be considered when selecting Coagulants and Flocculants for a Wastewater Treatment Facility?
- The composition and characteristics of the wastewater, including pH, turbidity, organic content, and the types of contaminants present, influence the selection of coagulants and flocculants.
- Treatment objectives, such as the desired level of contaminant removal and water quality standards, also play a role in the decision-making process.
- Cost-effectiveness, availability, and ease of handling and dosing are additional factors to consider when selecting coagulants and flocculants.
How can Testing and Analysis help determine the Optimal Combination of Coagulants and Flocculants?
- Thorough testing and analysis of the wastewater help identify the specific treatment needs and the most effective combination of coagulants and flocculants.
- Jar testing, for instance, involves conducting small-scale tests to determine the optimal dosages and combinations of chemicals based on the settling and clarification characteristics observed.
- By conducting these tests and analysing the results, treatment specialists can fine-tune the dosage and combination of coagulants and flocculants to achieve optimal performance.
- Additionally, testing allows for the evaluation of the potential interactions between the wastewater constituents and the selected chemicals, ensuring compatibility and avoiding any adverse effects.
What are the Environmental Benefits of using Coagulants and Flocculants in Wastewater Treatment?
- Coagulants and flocculants contribute to the preservation of clean water resources and the protection of aquatic ecosystems.
- By effectively removing contaminants from wastewater, these chemicals reduce the risk of pollution and the negative impact on aquatic life.
- Clearer and cleaner water discharged from treatment plants supports the health and biodiversity of receiving water bodies, creating a more sustainable environment.
What are some advanced Treatment Techniques that Incorporate Coagulants and Flocculants?
- Advanced treatment techniques that utilize coagulants and flocculants offer enhanced efficiency and effectiveness in contaminant removal.
- Membrane filtration, such as ultrafiltration or reverse osmosis, can be combined with coagulation and flocculation to achieve high-quality water purification.
- Dissolved air flotation (DAF) involves the injection of coagulants and flocculants to facilitate the flotation and removal of suspended particles.
- Electrocoagulation utilizes electrical currents to destabilize particles, facilitating their aggregation and separation.
How do these Advanced Techniques Enhance the Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment?
- Advanced treatment techniques provide additional means to enhance the removal of contaminants from wastewater.
- Membrane filtration offers a physical barrier to effectively remove suspended solids, microorganisms, and dissolved substances.
- Dissolved air flotation increases the efficiency of solids removal by creating buoyancy and facilitating the formation of larger floccules.
- Electrocoagulation allows for precise control over the coagulation process, improving the removal efficiency of a wide range of contaminants.
How can the appropriate choice of Coagulants and Flocculants address complex Wastewater Treatment Challenges?
- The appropriate selection of coagulants and flocculants is crucial in addressing specific challenges in wastewater treatment.
- Different coagulants and flocculants exhibit varying affinities for different contaminants, allowing for targeted removal of specific pollutants.
- By understanding the unique characteristics of the wastewater and tailoring the choice of chemicals accordingly, treatment efficiency can be optimized, even in complex and challenging wastewater compositions.
How do Coagulants and Flocculants contribute to maintaining clean Water Resources for future Generations?
- Coagulation and flocculation play a vital role in ensuring the availability of clean water resources for future generations.
- By effectively removing contaminants from wastewater, these chemicals help maintain water quality, supporting human health, agriculture & ecosystems.
- Through continuous research and innovation, coagulants and flocculants will continue to evolve providing more efficient and sustainable solutions for wastewater treatment, securing clean water resources for a sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, coagulants and flocculants are essential components in wastewater treatment processes. CoAg2-20A System is an advanced chemical treatment system, using the method of adding chemical coagulant and polymer to the treatment process, to efficiently remove suspended solids and emulsified oils from the water stream. Water Maze Water Treatment Systems have Water Maze systems are designed to clean the water used in high pressure cleaning or other applications. By considering factors such as wastewater composition, treatment objectives and operational parameters, the appropriate selection of coagulants and flocculants can address complex wastewater treatment challenges and contribute to maintaining clean water resources for future generations.
